hip dysplasia in babies test
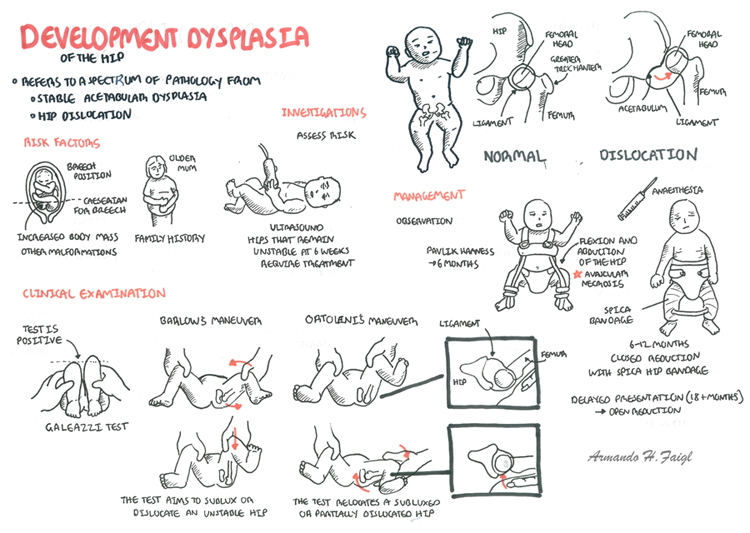
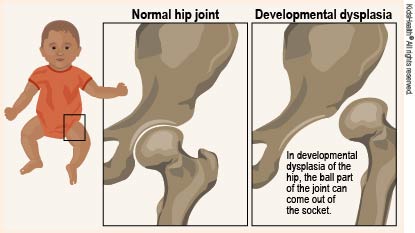
Routine neonatal screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip DDH is very important in all newborns. Hip dysplasia in babies also known as developmental dysplasia of the hip DDH occurs when a babys hip socket acetabulum is too shallow to cover the head of the thighbone femoral head to fit properly.

5 Causes Of Hip Dysplasia In Infants
When the ball of the hip is not sitting inside the socket of the joint but can be repositioned back.
. However DDH may not be discovered until later evaluations and not all hip dysplasia can be determined by physical examination alone. Doctors use a combination of physical exams and imaging such as ultrasound or x-rays to diagnose hip dysplasia. Your babys hips will be checked as part of the newborn physical screening examination within 72 hours.
It is named after Dr. When the ball of the hip can be pushed out of the socket of the joint using gentle pressure the hip. The childs hip will not develop normally if it remains unstable and anatomically abnormal by walking age.
This allows the hip joint to become partially or completely dislocated. Hip Dysplasia Presentations in the Walking Child Mild hip flexion contractures from bilateral dysplasia may produce hyperlordosis in the lumbar spine and a waddling type. Examine the hips by gently abducting and adducting each hip.
Standing at the end of the examination couch facing the baby. The affected leg may turn outward. Unilateral dislocations may produce a short leg gait andor limp in.
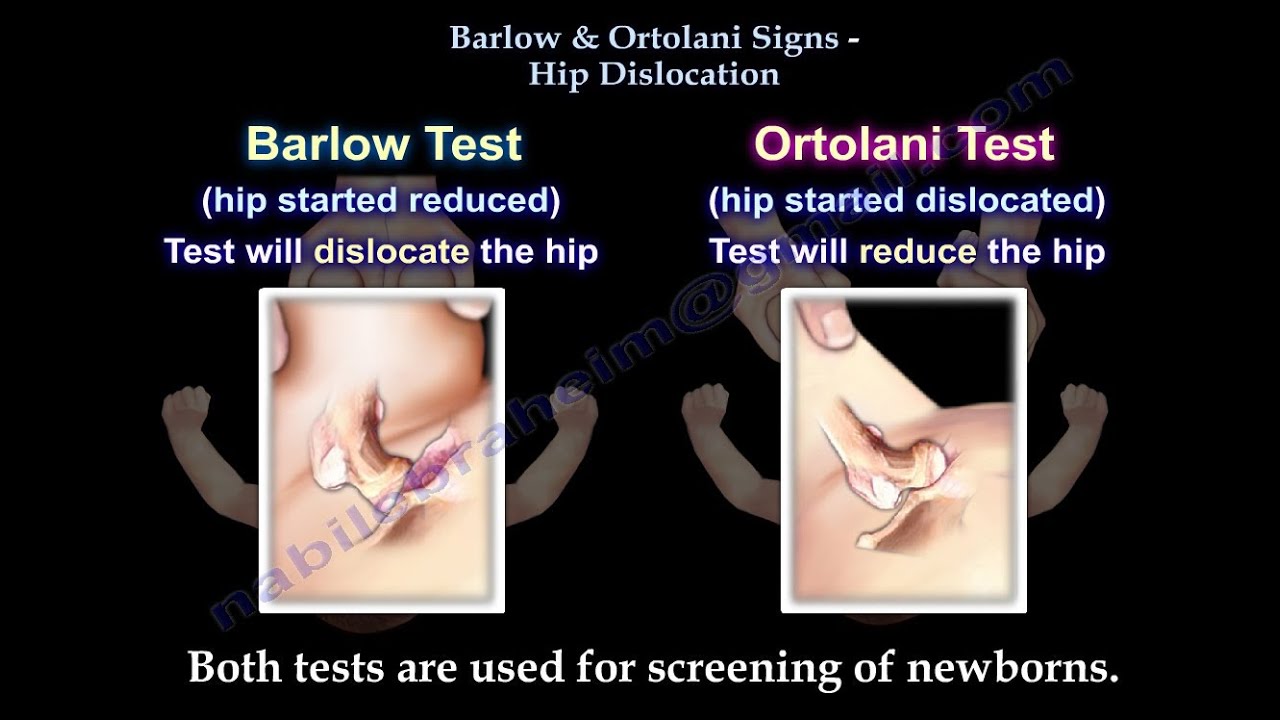
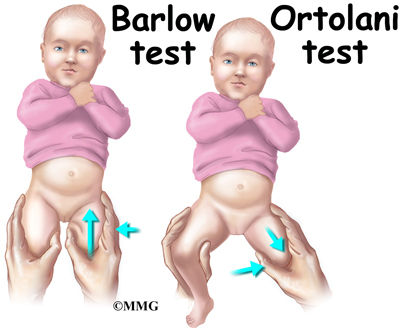
Popping sound with movement of the hip. One leg may appear shorter than the other. The Barlow test is a provocative maneuver used to reveal hip instability.
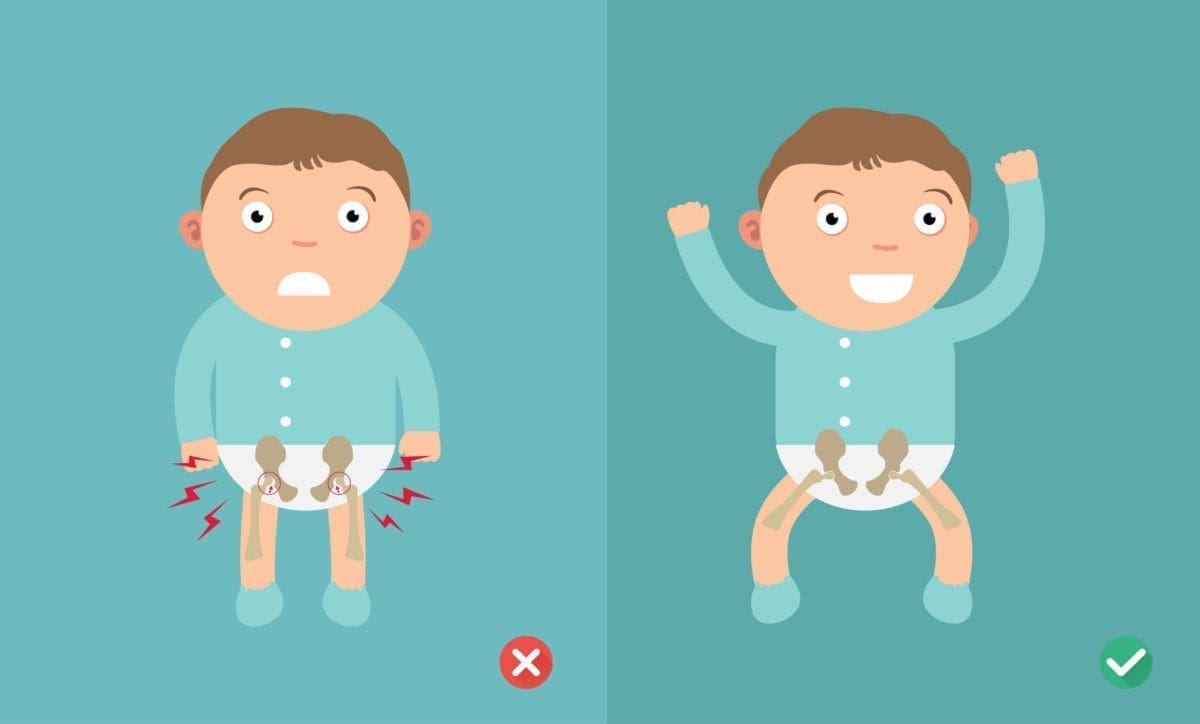
Babies are at increased risk for hip dysplasia in the following situationsThe baby is a twin. Quick Concepts are short videos that describe a key physiological or theoretical concept or demonstrate a brief procedureIn this video the viewer will lea. Developmental dysplasia of the hip Diagnosing DDH.
The US may reveal mild dysplasia that can spontaneously resolve after a few weeks of life. Onset hip dislocation still occurs in about 1 in 5000 infants by 18 months. Folds in the skin of the thigh or buttocks do not line up.
Developmental dysplasia of the hip DDH encompasses a spectrum of physical and imaging findings. Two tests are performed called the Barlow and Ortolani tests to examine the function of the hip joints. Signs and symptoms The leg on the side of the dislocated hip appears shorter or is turned outwards The folds in the skin of the thigh or buttocks appear uneven How is it diagnosed.
J Bone Joint Surg Br. A diagnosis of developmental hip dysplasia should be conÞrmed. Babies diagnosed with DDH early in life are usually treated with a fabric splint.
Httpsyoutube4-9FsXgDRDI Ortolani Method The Ortolani method is an examination method that identifies a dislocated hip that can be reduced into the socket acetabulum. DDH ranges in severity. It was renamed as there are different degrees of abnormality not just dislocated hips and it isnt always there from birth but can develop later.
If the hip feels normal but risk factors for DDH are present CHOP orthopedists recommend that screening ultrasounds be performed at 4-6 weeks of age. The Barlow manoeuvre test attempts to dislocate the flexed hip with a postero-lateral movement of the proximal femur. Perform hip examination should be performed within the first 3-5 days of life prior to hospital discharge.
Diagnostic procedures may include. Ultrasound Also called sonography - a diagnostic imaging technique which uses high-frequency sound waves and a computer to create images of the baby hip joint. Developmental dysplasia of the hip is usually suspected in the early neonatal period due to the widespread adoption of clinical examination including.
Developmental dysplasia of the hip DDH occurs due to an abnormal hip development which presents in infancy or early childhood with a spectrum ranging from dysplasia to dislocation of the hip joint. How is hip dysplasia diagnosed. Ortolani described the feeling of reduction as a Hip Click Examination of the newborn includes the Ortolani and Barlow method.
DDH was previously known as congenital dislocation of the hip CDH. Ordering ultrasounds for a child younger than 4 weeks can lead to false positive results. In babies with hip dysplasia the joint has not formed normally and the hips are prone to moving in and out of joint.
Hip dysplasia is the medical term for a hip socket that doesnt fully cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone. As the hips are moved in these tests a hip click can be felt by the examiner. After 3 months of age.
Hip dysplasia in babies can be difficult to detect because it typically does not cause pain but common symptoms may include the following. Hip clicks and asymmetrical folds are discussed in the older age group. Doctors will check your baby for signs of hip dysplasia shortly after birth and during well-baby visits.
Barlow Test edit edit source Barlows test identifies posterior sublimations or dislocation. Some babies have a. In 1978 ultrasound examination was introduced as a tool for detecting developmental dysplasia of the hip and evaluating infants with an abnormal physical examination33 Graf the pioneer in this.
Thomas Geoffrey Barlow who devised this test. Clinical Test for Hip Dysplasia Barlows Test -. Developmental dysplasia of the hip DDH is an abnormality in the hip joint usually present from birth.
Therefore careful physical examination of all infants to diagnosis and treat significant DDH i. 23 Risk Factors The strongest risk factors for DDH are breech presentation female sex and family history in a first-. This tests uses no radiation and is best.
Most people with hip dysplasia are born with the condition. Neonatal hip stability and the Barlow test. Ultrasounds and X-rays.
Physical examination using the Barlow and Ortolani tests are frequently positive in individuals with DDH. Perform Barlow and Ortolani manoeuvres on each hip. A study in stillborn babies.
Breech babies a family history of hip dysplasia and is known to occur more frequently in females. Department of Pediatric Newborn. With the former maneuver being the most important clinical test for detecting hip dysplasia in the newborn2.
The test is performed by. DDH refers to abnormal development of the hip where there is instability dislocatability of the hip and dysplasia abnormal shape of the acetabulum.
Hip Dysplasia In Infants Causes Signs Diagnosis Treatment

Hip Dysplasia Canadian Orthopaedic Foundation Canadian Orthopaedic Foundation

How Safe Are Babybjorn Baby Carriers Madeformums
Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip In Children Eorthopod Com
Developmental Hip Dysplasia Armando Hasudungan

Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Ddh Pediatric Ortho

Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Health
Hip Problems In Infants Familydoctor Org
Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip For Parents Nemours

Developmental Hip Dysplasia Children S Orthopaedic And Scoliosis Surgery Associates Llp

Congenital Hip Dislocation Or Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Causes Symptoms Tests
Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip In Children Eorthopod Com

Infant Hip Dysplasia Do Baby Carriers Cause Hip Dysplasia

Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Controversies And Current Concepts Bracken 2012 Journal Of Paediatrics And Child Health Wiley Online Library

How To Test For Newborn Hip Dysplasia By Nina Gold For Openpediatrics Youtube
Hip Dysplasia In Infants Causes Signs Diagnosis Treatment